Welcome to the top MBA directory in California. We have created the list of best California business colleges that provide BBA, MBA or DBA programs. Most business schools offer full-time, part-time and executive education. Such rankings are based on the student surveys, alumni reviews, admissions profiles, employment rates, average starting salary and peer school assessment. To find out detailed information about admissions and career about each school in California, just follow the link below.
- California Polytechnic State University-San Luis Obispo Orfalea College of Business
- California State University-Chico College of Business Graduate Programs
- California State University-East Bay College of Business and Economics
- California State University-Fresno Craig School of Business
- California State University-Fullerton College of Business and Economics
- California State University-Long Beach College of Business Administration
- California State University-Los Angeles College of Business & Economics
- California State University-Northridge College of Business Administration and Economics
- California State University-San Bernardino College of Business and Public Administration
- California State University-Stanislaus College of Business Administration
- Chapman University George L. Argyros School of Business and Economics
- Claremont Graduate University Peter F. Drucker Graduate School of Management
- Loyola Marymount University College of Business Administration
- Monterey Institute of International Studies Fisher Graduate School of International Business
- Pepperdine University George L. Graziadio School of Business and Management
- San Diego State University College of Business Administration
- San Francisco State University College of Business Graduate Programs
- San Jose State University Lucas Graduate School of Business
- Santa Clara University Leavey School of Business
- Sonoma State University School of Business and Economics
- Stanford University Graduate School of Business
- University of California-Berkeley Haas School of Business
- University of California-Davis Graduate School of Management
- University of California-Irvine Paul Merage School of Business
- University of California-Los Angeles Anderson School of Management
- University of California-Riverside A. Gary Anderson Graduate School of Management
- University of San Diego School of Business Administration
- University of San Francisco Masagung Graduate School of Management
- University of Southern California Marshall School of Business
- University of the Pacific Eberhardt School of Business
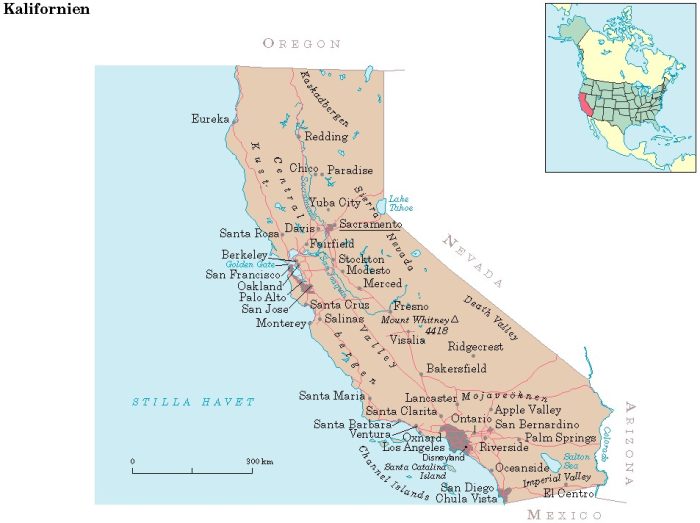
California, California, abbreviated CA, state of the western United States, by the Pacific; 411,000 km2, 39.6 million residents (2018).California, whose acreage is significantly smaller than Sweden’s, is the United States most populous state, and from an economic point of view a very rich area. The capital is Sacramento.
California. State Map.
Nature
California’s nature and climate vary greatly. At the far west is a narrow coastal plain. To the east of this, the coastal mountains rise with peaks exceeding 2,000 m above sea level. Between these mountains and the Sierra Nevada mountain range lies the Central Valley, which is drained by the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers and is California’s most important agricultural area.
California. Winery in the southern part of the Central Valley.
The Central Valley was probably formed during the tertiary period, when the bedrock was folded. The earthquakes that hit San Francisco are caused by movements along the San Andreas fault.
The mainly coniferous forested Sierra Nevada, which passes north into the Cascade Mountains, has the highest mountain in the United States outside Alaska, Mount Whitney (4,418 m asl). To the east of the Sierra Nevada lies Death Valley (86 m uh) and the Mojave Desert.
In the coastal area there is a Mediterranean climate with dry summers and some winter rain. The summer heat is somewhat mitigated in the north by the cold California stream. The mountain peaks of Sierra Nevada are snow-covered year-round, while Death Valley is one of the world’s hottest and driest areas.
California. Death Valley National Park.
Since 2011, California has been hit by a dry season that has caused several rivers, lakes and reservoirs to sink. The drought has also had major negative consequences for agriculture. In order to alleviate the water shortage, the state in 2015 imposed restrictions on the use of fresh water.
Vegetation varies greatly between different parts of California. In the north and along the Sierra Nevada, coniferous forests with Douglas fir and yellow pine grow and on the northern coast American sequoia, the tallest tree in the world. Along the coastal regions the rest are mostly macchia-like Mediterranean vegetation, so-called chaparral.
The fauna is very rich with black-tailed deer, black bear, cougar, sea otter, California sea lion (Zaʹlophus californiaʹnus), coyote, ground squirrel, turtles and rattlesnakes. California condor is endemic but on the verge of extinction; now it is only in captivity.
Population
California’s population of twenty was doubled during the 20th century; during the period 1980-90, the population increase was over 25 percent. Since then it has fallen slightly and during the 2000s the increase was just over 5 per cent, which is slightly higher than the US as a whole. Population growth was mainly based on strong immigration, both from other states and from abroad.
Ethnically, the population is mixed. Many are of Mexican origin, and the number of African Americans is the second largest (after New York) in any state. The Asian element is also significant.
California has the highest degree of urbanization in the United States. About 50 percent of the population lives in the Los Angeles region, and in the four largest metropolitan areas (Los Angeles, San Francisco, San Diego and Sacramento), over 80 percent of California’s residents live. The largest cities are Los Angeles (4 million residents, 2016) and San Diego (1.4 million residents).
Business
From an economic point of view, California is one of America’s leading states; GDP is highest among US states and in 2015, California accounted for just over 13 percent of US total GDP. In 2015, the state had roughly the same GDP as Italy. Just over 85 percent of GDP comes from the service and service industries, while the manufacturing industry accounts for 10 and agriculture for 2 percent.
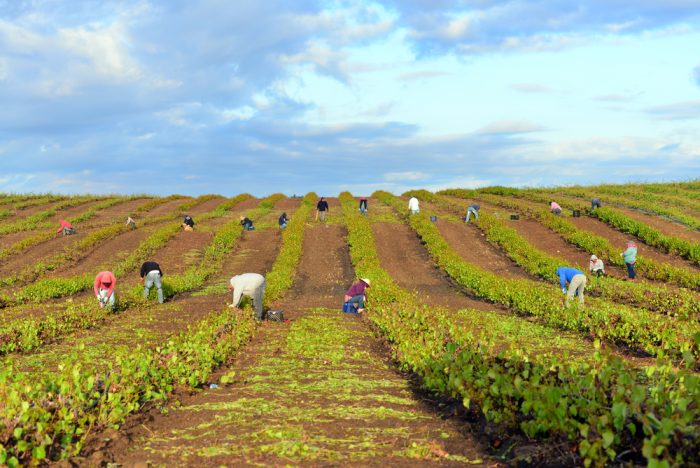
Agricultural production is the largest in the country, and it is complemented by a very significant food industry. Fruits (citrus and grapes), vegetables and cotton are grown on a large scale, mainly in the Central Valley and Imperial Valley (at the border with Mexico). The majority of the area is irrigated. Meat and dairy products play an important role; forestry and fishing have been of great importance. Gold was once the foremost mineral resource, but it has long been sought after by oil and natural gas.
California primarily has a lighter and high-tech manufacturing industry such as the aerospace and electronics and data industries with downtown Silicon Valley southeast of San Francisco. Other important activities are the federal military operations as well as the entertainment industry, with the film and TV industry concentrated around Hollywood and with Disneyland in Anaheim as one of many major tourist destinations. Research and development activities are of great importance. Stanford University (in Palo Alto) and the University of California (in, for example, Berkeley and Los Angeles) are prominent research centers.
Both passenger and freight transport are primarily by car, and California has the world’s best developed road system. With few exceptions, however, public transport is lacking. Despite stringent environmental requirements, California has very difficult problems with air pollution.
Tourism and gastronomy
Tourists looking for nature experiences, recreation and entertainment can choose from a variety of attractive destinations in California. However, the historical monuments are limited. Of interest are the 20 Spanish mission stations which, after 1769, were built from the current Mexican border and north along the coast to the area around San Francisco and connected by the so-called King’s Road (El Camino Real). It corresponded to roughly present Highway 1, which is considered one of the most scenic roads in the country. Some of the most visited old mission stations are in San Diego, Santa Barbara and Carmel. Memories from the Great Gold Rush can be studied inland east of San Francisco along Route 49, which is bordered by a series of old gold digging cities.
With its varied and partly grand nature, California can offer visitors the most diverse experiences. The main areas have the status of national parks or are otherwise protected. Yosemite is one of America’s most visited national parks with several million long-term visitors per year. The nearby Kings Canyon and Sequoia also have magnificent scenery and high visitor numbers. Further north in Sierra Nevada lies Lassen Volcanic with a very diverse and exciting nature as well as many hiking trails. The desert areas of Southern California can be studied from Los Angeles eastern suburbs or more in depth through visits to Death Valley. Pleasant recreation offers the many fine beaches along the Pacific coast, especially in the southern part of the state. Swimming and boating opportunities are also available around Lake Tahoe on the Nevada border.
Los Angeles and San Francisco are California’s major tourist center, where attractions with a focus on cultural life and the entertainment industry are concentrated. There are large museums, cultural events and numerous entertainment and recreation facilities. Popular tourist destinations in Los Angeles are Disneyland, Hollywood with movie studios and Beverly Hills with its luxury buildings. In San Francisco, the Golden Gate Bridge, cable trams, the former prison island of Alcatraz, the tourist-dominated Fisherman’s Wharf, and Chinatown are attracted. Also the capital of Sacramento and San Diego on the border with Mexico attracts many tourists, as well as smaller towns such as Monterey and Carmel south of San Francisco as well as Santa Barbara northwest of Los Angeles. Many Nordic visitors are also drawn to “Danish” Solvang (50 km west of Santa Barbara) and “Swedish” Kingsburg (30 km south of Fresno).
With its incredible wealth of all kinds of fruits and vegetables, California has long held a position as the United States Experimental Kitchen. Here you have not to a significant extent been bound by inherited traditions, by any pronounced lack of money and raw materials, here you have been able to mix well. Some surprising combinations may have occurred at first (peppers with orange, chicken with anchovies, crab with artichoke hearts), but many classics have sprung from this cornucopia (for example, Ceasar’s salad on binder salad, bread, parmesan cheese, anchovy fillets and Worcestershires fillets). with avocado, tabasco and chicken broth). Cioppino is a fish and shellfish stew with Italian roots, deviled crabbreaded crab meat seasoned with tabasco and mustard and then grilled. Of more traditional origin is the upside down peach cake and of course the ubiquitous sourdough bread, the sourdough bread which was a must for the golden eaters and which has retained its place as favorite bread. California is the United States leading state for wine production; see further American wines.
History
Already in the middle of the 16th century, sailors of different nationalities visited California, but only in the 1770s did the Spaniards begin to colonize the area. Then, among other things, 21 mission stations, which started farming with the help of the Indian people.
In 1822, California attacked Mexico in connection with this country’s liberation from Spain. Yet in 1846, the non-Native American population was only about 7,000, some of whom were North Americans.
The United States had begun to show interest in the area and took control of California in 1847, which formally joined the United States in 1848 after the victory in the war against Mexico. In the same year, a violent gold rush started, which in one year increased the population to over 70,000, which meant that California met the requirements to become a state. A dispute over whether slavery would be allowed ended with the inclusion of California in the Union in 1850 as a non-slave state. Subsequently, California developed rapidly with the mining industry and agriculture as the most important industries, especially since the transcontinental railroad in 1869 was completed and connected California with the rest of the United States. California had severe problems during the depression in the 1930s, but after 1945 a sharp increase in population has taken place, which in the 1960s made California the most populous state in the United States.
Politically, Republicans have long dominated, but since the 1950s, Republicans and Democrats have come to be relatively even.